
Examples include buildings, machinery, vehicles, office furniture, and land. The plant asset management market in the U.S. is growing significantly at a CAGR of 14.7% from 2024 to 2030. In the U.S., industries such as oil & gas, manufacturing, and energy are increasingly adopting predictive maintenance to improve operational efficiency.
Financial Accounting
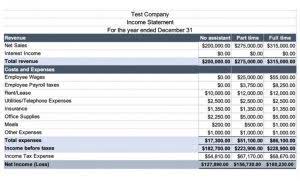
Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E) is a non-current, tangible capital asset shown on the balance sheet of a business and is used to generate revenues and profits. PP&E plays a key part in the financial planning and analysis of a company’s operations and future expenditures, especially with regards to capital expenditures. Delving into plant assets reveals an array of crucial resources, varying from the solidity of land to the sophistication of digital software. They form the backbone of a company’s operational arsenal, each with a distinct role and value on the balance sheet that can significantly impact long-term business success.
- Since plant assets have a finite useful life, they experience gradual wear and tear, which decreases their value over time—a process known as depreciation.
- The matching principle states that expenses should be recorded in the same financial year when the revenue was generated against them.
- Moving beyond software and donated equipment leads us into exploring how vital these resources are within everyday business activities.
- We offer Australians metalworking industry the best range of B2B Industrial Metalworking Machinery at Industry Direct Prices, supported by our strength in after sales parts accessories and service.
Defining Characteristics of Plant Assets
We always prefer to embrace the challenge of reinvigorating previous generation machinery to keep up to speed with the demands of modern manufacturing. Therefore, the first few years of the assets are charged to higher depreciation expenses. The later years are charged a lower sum of depreciation based on the assumption that lower revenue is generated. The resulting number of the PP&E equation tells investors whether the company believes in itself.

Reduce replacement costs and integrate seamlessly with durable asset tracking labels.
This not only reduces unplanned downtime but also helps in minimizing maintenance costs by addressing issues proactively. A key aspect of plant asset management is the implementation of aggressive maintenance plans and interval schedules. This proactive approach helps prevent breakdowns, reduce downtime, and extend the useful life of assets. By https://bio-max-plus.com/index.php/2021/10/20/correcting-accounting-errors-understanding/ carefully tracking and analyzing asset performance, businesses can make informed decisions about repairs, replacements, and upgrades, ultimately leading to cost savings and increased profitability. Plant assets are a group of assets used in an industrial process, such as a foundry, factory, or workshop.
Key Takeaway

Unlike inventory, which is held for immediate sale, or short-term investments, plant assets are foundational to a business’s ongoing operations. Generally, plant assets are among the most valuable company assets and tend to be relied on greatly over the long term. As such, these assets provide an economic benefit for a significant period of time.
- By utilizing PAM systems, businesses can make data-driven decisions that enhance asset performance, increase productivity, and optimize maintenance schedules.
- While depreciation is an expense, it is a non-cash expense, meaning it does not involve an outflow of cash in the current period.
- Countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asian nations are witnessing rapid industrial expansion, fueling the demand for Plant Asset Management (PAM) solutions.
- In contrast, plant assets represent long-term property expected to be around for at least a year, often quite a bit longer than that.
- Plant assets are an important part of a company’s financial structure, representing the tangible resources a business uses to generate revenue over an extended period.
A high asset turnover, relative to its peers, indicates a company is operating extremely efficiently. For example, a balance sheet might show “Property, Plant, and Equipment, Net,” indicating this depreciated value. As they will be used for more than one accounting period, they are subject to depreciation. The purpose of depreciation is to “charge out” a portion of the plant assets which have been used during the accounting period to generate business revenue.

What Are Plant Assets? Definition, Examples, & Accounting
- Buildings are vital for housing employees, storing inventory, or hosting customers, and they may be repurposed or expanded as a business grows.
- There are several methods to calculate depreciation, but all reflect how assets lose value over time.
- Various methods, like the straight-line or declining-balance method, are used to calculate annual depreciation.
- There are various types of assets investors must know about and can use to help determine good opportunities in the market.
- The cost of the machine is USD100,000, and it is expected to stay useful for five years with a residual value of USD10,000.
- Intangible assets are typically intellectual property developed by the company but could also be licensed from other parties on an exclusive or non-exclusive basis.
- However, we treat improvements to the land differently because they can wear out over time—like a new parking lot that needs repaving after years of use.
It’s very similar to the turnover ratio but looks at a company’s bottom-line profits instead of its top-line sales growth. You might have personal assets, like your house, a savings account, a life insurance policy, or a particular set of skills. A company’s assets, such as inventory, equipment, or patents, are more likely to be used plant asset to generate revenue. There are various types of assets investors must know about and can use to help determine good opportunities in the market. Plant assets are long-term physical items a company owns and uses to make its products, like buildings, machines, and equipment. The accountant debits the entire costs to Land, including the cost of removing the building less any cash received from the sale of salvaged items while the land is being readied for use.
Allocating Cost Over Time (Depreciation)
Any miscellaneous amounts earned from the building during construction reduce the cost of the building. Naturally, the initial purchase of the plant asset would be an outflow of cash, any subsequent sales would be a cash inflow. Thus, for plant assets accounting, it is necessary to understand and have a clear idea contribution margin about the above types of assets.
0 commenti